HYPERSPECTRAL REMOTE SENSING FOR DETECTION OF RHIZOCTONIA CROWN AND ROOT ROT IN SUGARBEET
Gregory J. Reynolds1, Carol E. Windels2, Ian V. MacRae3, and Soizik Laguette4
Graduate Student, Professor, Associate Professor, and Assistant Professor, respectively
1University of Minnesota, Department of Plant Pathology, St. Paul
2University of Minnesota, Department of Plant Pathology and Northwest Research & Outreach Center, Crookston
3University of Minnesota, Department of Entomology and Northwest Research & Outreach Center, Crookston
4University of North Dakota, Department of Earth System Science and Policy, Grand Forks
?
The soilborne fungus Rhizoctonia solani AG-2-2 causes Rhizoctonia crown and root rot (RCRR) of sugarbeet. The pathogen is becoming common and widespread in sugarbeet-growing regions of Minnesota and North Dakota because of increased acreage of soybean, edible bean and corn, which are also infected by R. solani AG-2-2 (5, 23). Thus, inoculum of the fungus is building up in soil and contributing to further outbreaks.
Severity of RCRR typically is assessed by a visual rating scale based on the amount of rot on the taproot. This traditional visual rating system, however, is destructive because entire plants are removed from soil. Furthermore, visual disease assessments are subjective in nature and affected by differences between individuals rating roots caused by fatigue, bias, and human error (13).
Remote sensing is an alternative method to non-destructively assess plant diseases rapidly, repeatedly, and over a large area without physical contact with the sampling unit (e.g., sugarbeet foliage) (13). It is based on measuring reflectance of electromagnetic radiation from a subject of interest, primarily in the visible (390-770 nm), near infrared (770-1300 nm), mid infrared (1300-2500 nm), and thermal infrared (2.5-15 μm) ranges (13). Instruments may collect either hyperspectral or multispectral reflectance data. Hyperspectral sensors measure reflectance contiguously as a series of narrow wavelength bands while multispectral sensors measure reflectance at a few wide bands separated by segments where no measurements are taken (17). Hyperspectral and multispectral wavelength bands obtained for plants typically are used to calculated vegetation indices that provide pertinent information (e.g., chlorophyll content) or to correct for background interference from soil or the atmosphere (21).
Remote sensing technology has been applied to the detection of numerous crop diseases, including Cercospora leaf spot (19) and Rhizomania (20) of sugarbeet. Aboveground symptoms of RCRR, including yellowing of foliage and sudden wilting of leaves, would be the basis for remote detection of this disease, but it also may be possible to detect stress in the plants before visible wilting occurs. Reduced photosynthesis rates or water content in sugarbeet plants could produce changes detectable with remote sensing instrumentation, but not the naked eye. Laudien et al. (10, 11) conducted research to determine the potential of remote sensing to detect RCRR, but the authors focused more on the distinction between healthy and unhealthy plants, rather than on the disease. They detected RCRR at the end of the growing season but did not address population of AG 2-2 (IIIB or IV), early-season detection of the disease, or the relationship of reflectance to severity of RCRR. Early detection of RCRR and/or the ability to assess disease severity based on remote sensing will allow assessment of entire fields for disease management.
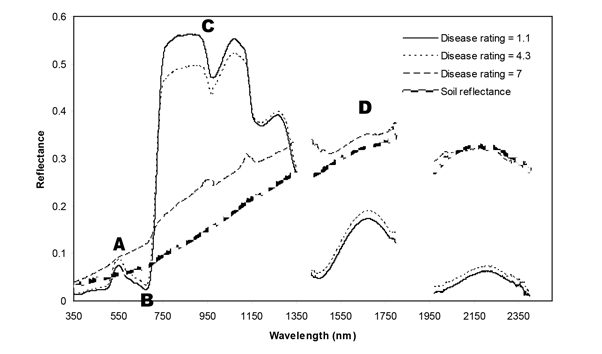
Examples of spectral signatures for soil background reflectance and sugarbeet canopy reflectance in plots with Rhizoctonia crown and root rot disease ratings of 1.1, 4.3, and 7 for the partially resistant variety (data collected August 18, 2008) where A.) is green reflectance (495-570 nm), B.) is red reflectance (620-750 nm), C.) is near infrared reflectance (770-1300 nm), and D.) is mid infrared reflectance (1300-2500 nm).
?
查看原文: